


Australian Biological Resources Study
| Checklist of the Lichens of Australia and its Island Territories | ||
| Introduction | A–D | E–O | P–R | S–Z | Oceanic Islands | References | ||
| Chapsa lassae Mangold | ||
in A.Mangold, J.A.Elix & H.T.Lumbsch, Fl. Australia 57: 653 (2009) T: near Rex Creek Swing Bridge, Mossman Gorge Section, Daintree Natl Park, Qld, 2995, A.Mangold 35zq; holo: CANB; iso: BRI, F. |
||
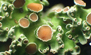
| Thallus usually epiphloeodal, in parts bulging and flaking away from the substratum, thin, to c. 100 µm thick, pale olive, glossy, smooth, continuous, non-rimose. True cortex thin, ±continuous, to c. 20 µm thick, of irregular to rarely periclinal hyphae. Algal layer well developed, continuous; calcium oxalate crystals absent. Vegetative propagules not seen. Ascomata conspicuous, to c. 0.6 mm diam., to, more often, irregular, apothecioid to chroodiscoid at maturity, erumpent, solitary or fused, often somewhat clustered, regenerating, immersed. Disc partly to, rarely, completely visible from above, greyish brown, indistinctly pruinose. Proper exciple not visible from above; thalline rim margin irregular, coarsely split, ±irregularly lobed, becoming distinctly layered in subsequent ascomatal generations, off-white to pale reddish brown, incurved to erect; outer layers becoming recurved. Proper exciple fused, thin, incorporating substratum material, hyaline internally to pale yellowish or yellowish brown marginally, non-amyloid. Hymenium to c. 80 µm thick, weakly conglutinated; paraphyses ±straight, moderately interwoven, the tips slightly to distinctly thickened; lateral paraphyses inconspicuous, to c. 25 µm long. Epihymenium hyaline, with fine greyish brown granules. Asci 8-spored; tholus initially thick, becoming thin. Ascospores transversely septate, fusiform to clavate, with ±rounded to subacute ends, hyaline, non-amyloid, 10–15 × 4–6 µm, with 3–5 locules; locules large, angular; end cells hemispherical to conical, divided by ±regular thin septa; ascospore wall thin, with a thick halo; endospore thin. CHEMISTRY: Thallus K–, C–, P–; no compounds detectable by TLC. |
||
| Known only from the type locality in north-eastern Qld; grows on tree bark in rainforest, at an altitude of 100 m. | ||
| Mangold et al. (2009) | ||
| Checklist Index |
| Introduction | A–D | E–O | P–R | S–Z | Oceanic Islands | References |
This work is copyright. Apart from any use as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, no part may be reproduced by any process without prior written permission from Australian Biological Resources Study. Requests and inquiries concerning reproduction and rights should be addressed in the first instance to Dr P. McCarthy. These pages may not be displayed on, or downloaded to, any other server without the express permission of ABRS.